Four Years After the Invasion, Ukrainian Leaders Build Foundations for Recovery
As Ukraine marks four years since Russia’s full-scale invasion, and more than a decade of war that began in 2014, the country is experiencing profound strain — millions are displaced, missile and drone strikes threaten energy infrastructure and cause frequent power outages, and there is a large-scale humanitarian crisis. As the country focuses on survival, defense, and endurance, an equal focus lies on laying the groundwork for long-term democratic recovery and postwar reconstruction.
Many of these efforts are being led by alumni of the Strengthening Ukrainian Democracy and Development Program (SU-DD) at Stanford’s Center on Democracy, Development and the Rule of Law (CDDRL). Launched in 2022 following Russia’s attack on Ukraine on February 24, the program brings mid-career Ukrainian practitioners to Stanford to develop implementation plans for projects focused on governance, recovery, and local capacity building. Participants engage with CDDRL faculty, global peers in the center’s Fisher Family Summer Fellows Program, and Bay Area tech and business experts, politicians, and government officials while refining strategies designed for real-world application under wartime conditions. The SU-DD program builds on the strong foundation of the Ukrainian Emerging Leaders Program (UELP), which was housed at CDDRL from 2017 to 2021. Between the two, the center has hosted 25 Ukrainian fellows across 7 cohorts.
After four years of war, SU-DD alumni say their work has taken on added urgency. Their projects now operate not as future-oriented plans but as active components of Ukraine’s wartime governance and recovery strategy.
From the Farm to the Front Lines
For Oleksii Movchan, a member of the Verkhovna Rada (Ukraine’s Parliament) and deputy chair of the parliamentary committee on economic development, his focus is on expanding financing tools for reconstruction. As part of a project he began during his 2025 SU-DD fellowship, he is drafting legislation to reform municipal bond regulations, aimed at increasing the participation of local governments in securities and debt markets and attracting additional resources for rebuilding Ukraine. To accomplish this work, he has relied on the Problem-Solving Framework he learned at Stanford, and shares that his experience in the SU-DD program made him more confident in his values and encouraged him to “stand on [his] principles and values of integrity, openness, and respect to human rights and democracy.” By strengthening municipal access to capital, his work seeks to support infrastructure recovery while reinforcing transparent financial governance.

Maria Golub, a senior political and policy advisor working on EU and NATO integration, is developing a national Coalition for Recovery — an inclusive, cross-sectoral platform designed to unify Ukraine’s defense, reconstruction, and reform agendas. With Ukraine balancing the demands of war and reconstruction, Golub’s 2025 SU-DD project aims to ensure that recovery planning connects security, governance, and innovation rather than treating them as separate tracks. Currently in a pilot, her proposals have already informed the government's 2026 recovery and resilience planning process.

At the regional level, Mykhailo Pavliuk, vice-chairman of the Chernivtsi Oblast (state) legislature in Ukraine, is actively implementing reforms to advance self-government and deepen Ukraine’s decentralization process. His work, initiated during his time at Stanford in 2023, focuses on strengthening “consolidated, self-sufficient communities” by developing political, financial, infrastructure, and social strategies that can be carried out locally, including cross-border regional initiatives in Chernivtsi. He said the most important element is “supporting the potential of people at the local level through the activities of advisory bodies, consultations, and modeling of joint decisions,” bringing citizens closer to decision-making on community affairs. Pavliuk emphasized that decentralization has been critical to Ukraine’s resilience since 2022, while noting that “there would certainly be a greater outcome in peacetime,” without the constraints imposed by war.

In the media sector, Alyona Nevmerzhytska, CEO of the independent outlet hromadske, is actively implementing her 2025 SU-DD project to strengthen the organization’s long-term sustainability and resilience. Her work, she says, “addresses two interconnected challenges: financial vulnerability and the rapid emergence of AI in the media landscape.” By developing diversified revenue strategies and integrating responsible AI tools into newsroom workflows, she aims to “improve efficiency, counter disinformation, and expand audience reach.” Despite ongoing security risks, she shares that the newsroom has maintained consistent production, adapted its operations, and prioritized staff safety, demonstrating what she described as “strong institutional resilience.” During her time on campus, Nevmerzhytska met with Stanford journalism and technology experts, whose guidance enhanced her strategic thinking around AI integration and digital modernization, “providing practical insights and [the] confidence to adopt responsible AI tools for efficiency and multilingual production.” She reports that hromadske continues to serve as a platform for accountability and public debate, reinforcing its role within Ukraine’s civil society.

Iaroslav Liubchenko, currently CEO of Ukraine’s national electronic public procurement system Prozorro, focused his 2023 Stanford project on strengthening transparency, efficiency, and institutional integrity in Ukraine’s defense procurement architecture. Today, that vision has become central to his leadership agenda. Prozorro is advancing three core priorities: deepening European integration through the approximation of EU public procurement directives into national legislation — in cooperation with Member of Parliament Oleksii Movchan — and sharing Prozorro’s digital governance model with EU partners; scaling up defense procurement within the system, including drones, unmanned and robotic systems, electronic warfare capabilities, non-lethal equipment for military infrastructure, and strengthened cooperation with the Defence Procurement Agency; and developing the broader Prozorro ecosystem through new coalitions and markets, advanced digital instruments, and AI integration. Prozorro seeks to ensure that Ukraine’s defense and rebuilding efforts are supported by transparent, technology-driven, and institutionally resilient procurement systems — not only fully aligned with EU standards, but capable of serving as a model for public procurement reform across Europe.

Ukraine’s Path Forward
Together, the fellows describe a future shaped not only by physical rebuilding but by the strength of Ukraine’s institutions and civic life. When asked about the country’s priorities for the next several years, their responses aligned in three areas: securing victory and sustaining defense capacity, advancing EU integration, and rebuilding critical infrastructure. Each emphasized that reconstruction must be paired with governance reforms to ensure public trust and long-term resilience.
Amid the political, economic, and human toll of war, our fellows agreed that the “unbreakable spirit and will of Ukrainians” gives them hope. “I am inspired by the endurance of Ukrainian society,” said Nevmerzhytska. “Despite exhaustion and loss, people continue to volunteer, innovate, and support each other. That civic resilience gives me confidence that Ukraine’s democratic spirit remains strong.”
As we look to the beginning of the fifth year of Russia’s war, Ukraine’s future is still uncertain. But the projects these leaders developed during their time at Stanford have carried into their work in parliament, regional government, civil society, media, and the defense sector. What began as ideas for reform are now being tested and adapted under wartime conditions, as they work to keep institutions functioning and prepare for the country’s long-term recovery.
Read More
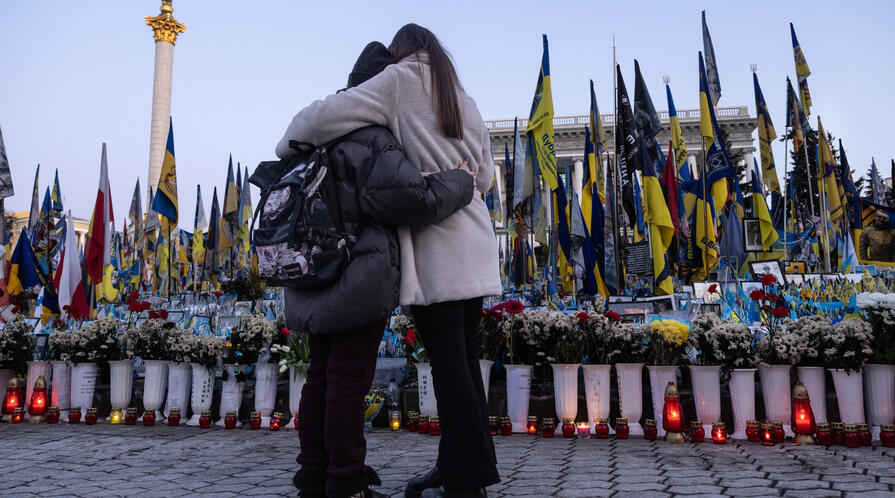

From parliament to regional government to independent media, alumni of the Center on Democracy, Development and the Rule of Law’s Strengthening Ukrainian Democracy and Development Program are implementing reform initiatives under wartime conditions.
- Stanford’s Center on Democracy, Development and the Rule of Law (CDDRL) launched a fellowship in 2022 to support Ukrainian leaders in designing governance and recovery reforms.
- Alumni of the Strengthening Ukrainian Democracy and Development Program (SU-DD) now implement those plans across parliament, regional government, media, and defense procurement.
- Stanford-developed reform strategies now support Ukraine’s institutional resilience and transparent recovery during wartime.



















![Oleksandr Sereda [left] and Artem Romaniukov [right] during their campaigns for, respectively, city council and mayor in Dnipro, Ukraine in the summer of 2020.](https://fsi9-prod.s3.us-west-1.amazonaws.com/s3fs-public/styles/717x490/public/artem_romaniukov_ukraine_mayor.jpg?itok=AHyGRtgy)




![Oleksandr Sereda [left] and Artem Romaniukov [right] during their campaigns for, respectively, city council and mayor in Dnipro, Ukraine in the summer of 2020.](https://fsi9-prod.s3.us-west-1.amazonaws.com/s3fs-public/styles/1300x1300/public/artem_romaniukov_ukraine_mayor.jpg?itok=pgwenUv9)











 "Identity" hardcover book by Francis Fukuyama
"Identity" hardcover book by Francis Fukuyama
