Hope, Despair, and the Emotional Response to the War in Ukraine
The war in Ukraine has been a roller coaster of emotion for many in Europe, particulary for Ukraine's closest neighbors and allies. Among these are Gabrielius Landsbergis, the former minister of foreign affairs of the Republic of Lithuania, who was scheduled to visit Kyiv the day Russia's full-scale invasion began.
Landsbergis joined Michael McFaul to discuss how Europe has been emotionally and politically navigating changes on the battlefield and attitudes about the war in government halls around the world, and explains what he believes needs to be done to develop long-term strategies of support for Ukraine.
Gabrielius Landsbergis is currently based at the Freeman Spogli Institute for International Studies at Stanford University, where he is the Bernard and Susan Liautaud Visiting Fellow. Previously, he has served as the chairman of the Homeland Union Party while concurrently a member of the Lithuanian Parliament. Before assuming these roles, Landsbergis was also a member of the European Parliament and began his career as a diplomat for the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Lithuania.
Listen below to hear Landsbergis' discussion with Professor McFaul, which was originally recorded during an event hosted by the Center for Russian, East European & Eurasian Studies, Stanford University Libraries, and the Freeman Spogli Institute for International Studies on December 10, 2025. World Class is also available on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, and other major podcast platforms.
TRANSCRIPT
McFaul: You're listening to World Class from the Freeman Spogli Institute for International Studies at Stanford University. I'm your host, Michael McFaul, the director of FSI.
Today I'm sharing a conversation I had with Gabrielius Landsbergis. He is the former Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Lithuania, and he is currently here at the Freeman Spogli Institute as our Bernard and Susan Liataud Visiting Fellow.
Gabrielius has an extremely impressive resume, and we can't go through it all right now, but he's been instrumental in pursuing a values-based foreign policy in Lithuania and the European Union. He is also one of the most vocal supporters of Ukraine, Taiwan, and freedom fighters worldwide.
We had the opportunity to discuss not just the diplomatic and political ramifications for Europe of Russia's war against Ukraine, but also the emotional journey this war has had for many people in Lithuania, including Gabrielius.
This was a very unique, often poignant conversation, and I hope you'll take away as much from it as I did.
[BEGIN EVENT RECORDING]
Before we get into the questions that I have that we agreed to talk about, I first just want to get your explanation of the title of this talk. It's an interesting title. Why did you choose it?
Landsbergis: Well, first of all, it's a great honor to be here, to speak to the people who are interested in the topic of Ukraine, that's mainly at the core of it, and the war that's ongoing.
I'm really honored to be at Stanford for the year. Thank you so much for kind words. It makes me blush every time.
When I was thinking about the topic, I was thinking for the first time as a bit of an observer.
McFaul: Because you used to be a participant.
Landsbergis: Yeah, it felt like one. So, the war started in 2022 when I was a minister. I was fully in my office when I got the news. I was supposed to travel to Kyiv the same day, February 24th; I had a ticket to go to Kyiv.
McFaul: Really?
Landsbergis: Yeah. I went to the airport and the flight was canceled at 5 a.m. And I called the chief of staff of the Lithuanian Army and they said, this is it. This has started.
So the opportunity to travel to California to stay at Stanford allowed me a step back. Even though my mind is fully with the people who are fighting for their country—basically that takes all my thinking time throughout the day—but still one has an ability to reflect.
And what I reflected is that there is an amplitude of emotion when we observe the war. It started with a shock, with the first sights of burning buildings in Kyiv, Russians crossing the borders and just flowing in, like really existential threats.
Then it was changed with some sort of a relief or even a joy that Ukrainians were able to push back. Then it picked up when the counter-offensive started and when Ukrainians started pushing Russians out. I've seen people who are like watching this as if they were winning. We were winning. This was part of our victory. It felt as if any one of us could go to the front and help Ukrainians just to finish this off and restore the normality, restore something that we were afraid that we were losing.
And then it was changed again. The first signals that the West is unable to support to the extent that is needed. Russia threatening with a nuclear (possible) nuclear strike. The West taking it very seriously [and] stopping Ukrainians moving forward. And then the question, okay, so what's next?
And then when I came back here, the information that reached us was that the one that Ukrainians developed new weapons. They've developed long range missiles. They developed the ability to strike deep within Russian territory. Apparently the allies have removed the restrictions on the strikes and Ukrainians have been very successful with that.
So the first thing that I would do: I open whatever social media I'm using that day and one of the first messages there is, “New factory is burning.” It's like, oof, okay, so we still have cards. We're in this and it's not over. Even though it was said in the Oval Office that that's it, Ukraine has no cards. We do have cards. And “we” as those people who are deeply supportive of Ukraine.
And then came Alaska, now the peace plan. And again, we're over the hill and down to valley, so to say, of emotions.
So I was thinking about this trajectory because there is a lot of emotion into this. So how do we deal with that? How do we stay on the line? How do we explain to ourselves where Ukraine actually is, what actually needs to be done, and how we can continue supporting despite what the headlines are telling us today? So we don't give in to overjoy that, Okay, this is won, this is fine, like we did in late 2022.
Or we don't give in to despair like it happened a number of times when the front is breaking or one important point on the front line is being lost.
McFaul: Step back for a minute and talk about not emotions, but objectives. To the best of your knowledge and guessing—these are difficult things to establish—what are today, Russia's interests and objectives in the war? What about Europe? What is your assessment of American interests? I'm kind of curious what you think about that because I'm not quite sure what they are. And maybe they're self-evident, but I don't think they are: maybe say a little bit about what you think Ukrainian objectives are today.
And as you go through that list—and maybe add China too if you want; I think that could be interesting to hear your view on China—and as you do so, also do you think they've changed over time? Most certainly the American objectives seem to have changed with our election, but maybe not. I don't want to presume that I know that. Or have they been consistent over time since the full-scale invasion began?
Landsbergis: So first of all, think that one country that has not in no way changed their objectives is Russia. Their objective is subjugation of Ukraine or Ukrainian country. Full control, either physical or political control, any way they can exert it. That might require them conquering the whole country. That might require just creating enough instability so that the country is ungovernable and would be basically then controlled in a similar way like, for example, Georgia now is. Russians did not need tanks to take Tbilisi; they managed to do that in a different form. Even though people are still protesting there, the country is ruled basically by a Russian proxy.
So, this is still their goal. It could be political. It could be that Putin's mandate, the way that he structured his mandate, why people do support him, why his circle of oligarchs continues to support him is because he can bring victories. And this is still required and he still has this goal.
But there is also a practical element in this. I try to imagine if there would be a ceasefire signed between Ukrainians and Russians. Just imagine: 2,000 kilometers of frontline. 2,000 kilometers is like half of Europe from Vilnius, from Lithuania's capital, all the way to Amsterdam. That's how much frontline there is.
So to maintain a ceasefire on that extensive frontline, you basically have to have an enormous amount of trust that the other side will not counter attack. I very much doubt that Putin has that trust on Ukrainians and vice versa, right? So both sides will be forced to keep and maintain the force presence on a frontline just in order to make sure that the frontline is not moving. And Ukrainians have showed that they're capable with Belgorod.
It's almost couple of years ago when they crossed the Russian border and attacked a Russian territory, taking a bit of Russian Federation as a leverage for the possible upcoming negotiations. So, Ukrainians show that they have the capacity.
Thinking about that, Putin will have to maintain about a million peoples army, as much as he has now, on the front line to make sure that the front does not progress. Or he needs Kyiv. So, that's why I believe that in his mind, a ceasefire will not work.
And that's why he was pushing back on American efforts to offer a ceasefire. When President Trump suggested that, he said, well, I need a comprehensive peace agreement with everything that I set out to achieve. This is what I need. And the reason is it could be very practical because the ceasefire will just not work. He will never trust Ukrainians. And he doesn't want to maintain troops. If he wants to let troops do something else, attack another country, turn back home, whatever that he has on his mind, he needs Kyiv where he wants that.
So whatever comes out of any talks now, I'm pretty convinced that Russians have not moved with their goals. And they believe that they're successful with that. That's number one.
So I will jump over to Europe. Europe is developing its goals. My biggest criticism of Europe that we've set out to support Ukraine without a clear plan as to what we want to achieve. Like, what is our goal?
Do we want to stop Russians? Do we want to push them back? Do we want Ukraine to win? Do we want to restore the deterrence of the European continent with European Union on one side, but allies kind of also in this hold? What is our plan? So we paid up without knowing what we are buying.
So we bought some time. With a lot of money, we bought some time. We bought four years. But we have not developed a strategy. The reason could have been is that we've outsourced the strategic thinking over to the other side of the Atlantic.
We said, “Okay, fine, we'll pay the bill. There are people in Washington who will know how this should end. We might not like it, but we still trust that it's probably the best outcome.” And that has been happening through with the previous administration, where Jake Sullivan was the one saying the strategic defeat of Russia is in the transatlantic goal. Again, that was the only time that I heard somebody suggesting a strategy.
With the change of administration, there is no longer a strategy. And Europe is now figuring out that we have to have something. That's why you see Europeans scrambling for money. Because we don't have a plan for next year. And the only way to have a plan for next year is to have something we could finance it with.
And that's why we need frozen Russian assets. That would help us finance for next year and maybe a couple of years in the future. That is the first shape of the European strategy to Europe. I hope that it will have other steps. I'm still hoping that we have enough time.
For Ukraine, the strategy, you might say, that it has not changed fundamentally: it's to defend the sovereignty of its country. Certain elements have moved. First of all, was claiming back all the territory, 2022 autumn. Ukrainians have declared that our goal is to go all the way back to Crimea. Now this is no longer a goal. And honestly, I do understand them. They have a strategy, right? They had a strategy, but it very much depends on [if] our strategies are aligned, if we see the same way, and if we're going to help them to achieve their strategy.
Unfortunately, they were not aligned. And that means that they are unable to achieve certain goals. And Zelensky was brutally clear yesterday in his interview, suggesting that, unfortunately, the plans changed. We cannot get to NATO because there is no path for us going there. We cannot reclaim Crimea and so many other things.
I mean, it breaks my heart to listen to that. For me, it's very, very much 1938, a speech by Czechoslovakia's president saying, certain things were forced on us and we're just unable to withstand pressures from two sides. And this is where Ukraine currently is.
I could talk about China, but I mean, it will take another 20 minutes.
McFaul: Well, let’s come back to China, because they're peripheral. But you haven't seen any change in their behavior, have you?
Landsbergis: I think I do see. Many people do argue, and I participate in number of conversations where people would argue that saying, “Well, for China, they need a stable world. And they need Europe stable because it's a good client for whatever they're selling and they require stability.”
And I'm not so sure whether that's true any longer. They built up an enormous, extraordinary leverage on Russia as it is now.
When experts say that 90% of Russian military output is produced with Chinese help, either equipment or material or just produced in China, that tells me that if you remove that, Russia would be unable to fight against Ukraine, not at the extent that they are doing it currently.
So that means that China actually is invested in the war. That actually they want the war. So that raises a lot of interesting questions. So that means that instability in Europe works in their benefit.
And I mean, even in stable Europe, just the recent quarter numbers, German imports of Chinese goods has risen by 14% in just the last three months. That's biggest in the world. So even unstable Europe is a rather good client.
McFaul: So they have their cake and eat it, too.
Landsbergis: Yeah. And they are probably getting other cakes that we can only kind of try to imagine or I mean, try to understand what those are. One of them [is] building up a leverage on Russia where you can call the credit back either in Indo-Pacific or actually keeping Europe occupied. I mean “busy.”
McFaul: Talk a little bit about the U.S. and the piece that you wrote in the New York Times and what is your analysis—I'm asking not for your opinion about what should be the U.S.—we'll get to that later. Analytically, what do you think the Trump administration is trying to achieve right now?
Landsbergis: Well, that's probably one of the most difficult questions that there is. Honestly, when the administration took over, I tried to understand, tried to read the administration's mind as a European. And there are certain elements that I do understand.
It's very difficult to explain to an American why Europe is unable, like completely unable to deter Russian attack. A continent of 450 million people, if you add United Kingdom, more than half a billion people. Probably one of the richest places in the world.
And we are seeing Ukraine, a country of 40 million people, that was able to stop Russian attacks. Or at least to slow it down significantly in order to retain its sovereignty for a number of years. And then the continent of 450 million says, “Well, unfortunately, there is nothing that we can do.”
You're unable to square this. So when we hear criticism, or at least a question like, guys, are you sure that there is nothing that you can do? I cannot answer that. I only can say, yes, there are things that we can do. We should be doing them. We should have been doing them long, long ago, probably when President Obama suggested that United States will be pivoting over to Indo-Pacific.
That was the beginning of it. This is where we should have started our rethinking of a European strategy. We did not do it. It's on us. We'll fast forward it now and we'll figure things out.
I understand that Europe has to become stronger. I understand that Europe has to find ability to deter Russian attack to help its allies and make a proposal to United States why a strong partner is a better partner.
This is the part of the strategy, the part of thinking that I understood as a strategy. Now the recent documents that have been announced, they talk about very different point of view. They talk basically about weak Europe, about divided Europe, about a Europe of Hungarys that would all look just for their own interest. No united Europe, no Europe that could be able to figure out its united budget of defense.
If this is the vision of Europe, this Europe will be purchasing Russian oil and gas the same way that Hungarians are doing. This is the Europe that will not be able to help Ukraine as much as Hungary has blocked almost all the attempts of Europe to do that. This is the Europe that will not be a good partner for United States, either deterring China or stopping Russia or basically doing anything. This is the Europe that would be susceptible to Russian attacks, that will be susceptible to Chinese interventions, economic or otherwise. The weak Europe that is suggested in the latest strategy document is a very scary perspective for Europe.
It's very difficult to understand why that would be in the interest of the United States. That's probably the most difficult question to answer. Maybe it will be explained in some way. People are trying to square the circle, and I've seen Sir Elbridge Colby trying to explain that it's still the same strategy. We still want a strong Europe.
McFaul: It wasn't in the document, though.
Landsbergis: Yeah, wasn't in the document. So, for a European, it's very difficult to understand that. It doesn't change the fact that Europe has to get its act together.
And my piece in New York Times argued that basically the way that I see is that there are things that we just cannot change in the United States, and we shouldn't be attempting that. In many ways, President Trump, for us, is a force of nature. We are not participating in the election. We won't be. We don't have a vote. So we just have to accept whatever he considers is in the interest of Americans.
But that doesn't mean that there are nothing that we can do. We can make a very good proposal to American people [to] have a strong partner in Europe. Be successful. I argue that nothing brings success as much as success. And we can do that in Ukraine. We can do that with our own defense. And kind of I have a sense that if there's something that could convince [the] U.S. administration to turn around and look differently at the European Union, that would be us becoming stronger.
McFaul: Well, I agree with you, by the way. And I am an American; I do get to vote, unlike you.
And I do think this is a debate we need to now have now that this national security strategy has put it out so baldly. I've been traveling around the country talking about my book. And in the conversations later, I sense that people like me most certainly, but maybe also Europe needs to make the case— I'm just restating what you said, but in a more America-centric way—about why Europe is so good for us. I think we've taken advantage of that and we've forgotten what the arguments were, kind of original purposes.
But come back just for a moment on the Ukraine part. What do you think this latest rounds of negotiations are they trying to achieve? What's the outcome they desire? Is it just simply they just want to end the war and let the president say he ended the war? Or is there something bigger at stake?
Landsbergis: You mean U.S. effort?
McFaul: U.S.effort, yes.
Landsbergis: I'm thinking that probably for some in the current administration, the war in Europe is a distraction. It’s a distraction for what's really happening in the Indo-Pacific and the worries that are growing there.
So it's a kind of a cut loss situation. And there's no better strategy, right? This is what President Trump has always been saying. And even in yesterday's interview in Politico, he said, “Well, if Europeans do have a strategy, they should come forward with it.” And to our embarrassment is like, yeah, we have not figured that one out. So what do you expect, right?
So it's the best strategy in town. It's a horrible strategy for Ukraine. It's a horrible strategy for Europe. It basically increases the chance of Russian attack on Europe tremendously, at least from my perspective. If he's given, if he's rewarded for his attack of 2022 and 2014, that will only increase his thinking that he can continue with that. But it's on Europe
Now we need to figure out what we're going to do with it. And then in this, well, President Trump is doing what he does, right? So if you don't have a better plan, that's my plan is the only one that I have.
So Russia’s not in good place with this. U.S. basically is just . . . I usually call that a shift, shifting from Europe, from European security area, wider security area, meaning that it's larger than just NATO. And Ukrainians are basically cornered with very little things that they can do.
I've heard, again, it was written out that Zelenskyy spoke with the European leaders, and he said that he's extremely worried that if Europeans will not figure out the frozen assets. That's basically the last thread for Ukrainians. If that gets figured out, then Ukrainians get in a stronger position. Then they have a lifeline, know, some more runway for two, three years to figure things out. If they don't have that, then this is it.
McFaul: That debate, in my view, is so tragic. I run an international working group on Russian sanctions, and we’ve published 23 papers on how to increase sanctions over the last three and half years.
In October of 2022 was when we published a paper about these assets. We're still debating these things. That just doesn't seem strategic to me.
And this thing that you've talked about before, that we're constantly worried about escalation from Putin And you noted that the biggest moment was in the fall of 2022 when allegedly he threatened to use nuclear weapons. But then we do so many things that I just don't think are in our own national interest.
So you've hinted at this, but I want to hear you one more time on your sense of, even more emotionally, to use the title of the talk, of the sense inside Ukraine. Your colleagues there, what you're reading, does this feel like the valley? Obviously it is. We get that. But is it this last valley, and that they're just going to have to capitulate? Or is there other things that, I mean, the assets is one of them, maybe weapon systems that are coming on board, that you hear gives Ukrainians hope right now?
Landsbergis: Well, I've never heard Ukrainians complaining. I can tell a short story which defines the spirit of Ukraine. So that was in 2023, Vilnius was supposed to host [the] NATO summit and President Zelenskyy did a tour in the Baltic states to talk with the countries about what to expect from [the] NATO summit.
And prime minister of my country, my good friend, she invited me to participate in the meeting which she had with the president. During the meeting, she gave me the floor and I said, “Well, unfortunately, Mr. President, I'm doing the diplomatic rounds in Europe and NATO. And as an upcoming host of events in Vilnius, there are not too many things that I can promise. And if there is a saying about the glass being half full or half empty, my glass is almost empty, preparing for NATO summit.”
And I meant that most of the promises or belief that they had, the invitation coming over or, something substantial being announced . . . it's just not happening. There's just too many divisions within the alliance.
And Zelenskyy reacted in a very Zelenskyy way. He took his bottle of water and said, “Do you want me to pour you some?” And this is what Ukraine has always been.
I've been fourteen times in Kyiv after the war started.
McFaul: Fourteen times?
Landsbergis: Yeah.
McFaul: Wow.
Landsbergis: And every time I go over there, I said, I'm really depressed. I mean, this is looking so bad. And they're like, no, it's not that bad. We're fighting. Donbas has not fallen. Kyiv is standing. And now they're saying we're fighting corruption. Bad guys lose. We still have a hold of it.
I mean, it's incredible. It's incredible. If you want to lift your spirits, just talk to a Ukrainian. They will tell you the most horrible stories that they're undergoing, and they will still be upbeat. That kept me up and lifted me up and never allowed me to get into despair.
And today is exactly the same story. Yeah, the allies betray. Some of them walk away. Some of them change their attitudes. But nothing has been lost yet. That is their attitude. I'm pretty sure that they are. And it actually there is a political element to this.
So when people are saying, well, Zelensky can just give Donbas and let it go. Ukraine is a democracy. And that means that the president is mandated, very strongly, democratically mandated by its people. And people do not believe that they should be letting the territories that are not under Russian occupation go.
And these are the civil society, the so-called Maidan people who are still very much there, who walked over to the streets last summer during the war protesting against the reform of the anti-corruption agencies and told the government, you cannot do that. We're against this. And [the] president retracted.
These are the frontline warriors who spent decades in the front line digging in, fortifying the cities in Donbas. And I don't imagine them letting that go. And they mandate, democratically, the president. So, and when Zelenskyy says, “People will not allow me to do that,” this is not a way to politically get away from a pressure. That's a reality. His political mandate does not allow him to do that.
And this is what upsets me when the Coalition of the Willing meets, takes a picture and suggests, well, we're talking about security guarantees. Ukraine can mostly depend on Ukrainians. This is their thinking. This is not a way to do it. Ukraine needs true commitment. Ukraine needs Western commitment, no longer just words.
If we want to make sure that this peace holds, that the Russians don't attack, that we have to tell Putin that the next time you attack, you are going to meet, like President Macron suggested, French troops in Odessa, Polish troops in Kyiv, Lithuanian troops together with Poles and German air force, whoever is willing to give their equipment or people for the cause.
That is the statement that Ukrainians want and I'm pretty sure that this is the thing that is required. Are Europeans ready to do that? Well, I have not yet seen the signals that would encourage me.
McFaul: Well, that's a downer note in the valley of emotions, just like you said. But I want to end on an optimistic note.
As an American who believes that my country is stronger and more secure and prosperous and free with strong European allies, it's one thing to like debate these things abstractly when you've never been to Europe. But when you meet leaders like Gabrielius, how can you not be inspired about a future with guys like him in power in Europe? That's a world I want to be a part of. And that's why I'm so grateful that you're here with us at Stanford today.
Landsbergis: Thank you.
McFaul: Thank you!
[END EVENT RECORDING]
McFaul: You've been listening to World Class from the Freeman Spogli Institute for International Studies at Stanford University. If you like what you're hearing, please leave us a review and be sure to subscribe on Apple, Spotify, or wherever you get your podcasts, to stay up to date on what's happening in the world, and why.
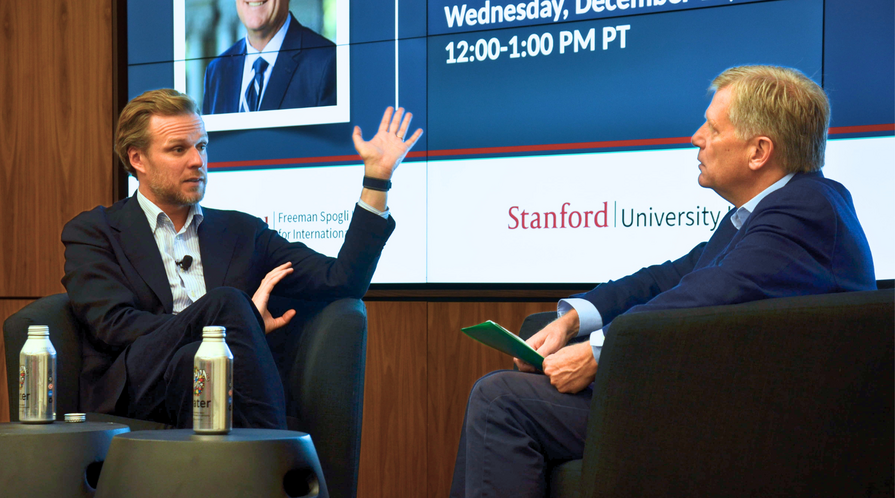

On the World Class podcast, Gabrielius Landsbergis shares what the war in Ukraine has looked and felt like from a European perspective, and what he believes must be done to support Ukraine for the long-term.